Dr. AbhayRaizaday2Madhuri Patil (Mohite) 1, Ms. Sharda Yesade3
School of Pharmacy, Suresh Gyan Vihar University Jaipur, Rajasthan
Gourishankar Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Limb, Satara. Maharashtra
Corresponding Author E-mail: msmohite.2008@yahoo.com
Contact mobile number: – 9960426837
Abstract: Continuous development in new drug delivery systems plays an essential role in the Pharma industry. There are various controlled-release products available in the market, Microsphere is one of them. Microspheres are small spherical free-flowing powders. Diameters typically range from 1 µm to 1000 µm. Microspheres can be produced by using polymers obtained from natural and synthetic sources. Based on the method porous or solid microspheres can be obtained for specific intended applications. The study mainly includes various aspects of microspheres, method of preparation, evaluation parameter, efficiency, and applications. Microsphere targeting various types of diseases including diabetes, cancer, antioxidant, cardiovascular disordered, Hepatotoxicity, etc. In the present study, Microspheres were prepared with cinnamon oil using the solvent evaporation method. Prepared microspheres were evaluated for particle size by micrometric technique and shape.
Keywords: Novel Herbal Drug Delivery, Microspheres, Cinnamon oil, Applications, Evaluation.
Introduction: Novel drug delivery system refers to the approaches, formulations, technologies, and systems for transporting a pharmaceutical compound in the body as needed to safely achieve its desired therapeutic effects. Several types of NDDS have been developed during the last few decades which are- Microparticles, Nanoparticles, Osmotic ally Modulated Drug Delivery Systems, Transdermal Therapeutic Systems (TTS), Aqua some, Dendrimers, Multiple Emulsions, Microemulsions, Liposomes, Noisome, Self-Regulating Drug Delivery, etc. (1)
Microspheres have free-flowing powder characteristics, which are consisting of synthetic polymers and proteins. These are biodegradable in nature having a particle size of less than 200um. Microspheres are the multiparticulate drug delivery systems which are consisting of natural and synthetic materials. Microsphere enhances stability, and bioavailability and also targets the pharmaceutical drug to a specific site at a preset rate. Microspheres are particularly used in novel drug delivery systems. (2)
Types:
- Floating microspheres
- Biodegradable polymeric microspheres
- Radioactive microspheres
- Synthetic polymeric microspheres
- Bioadhesive microspheres
- Mucoadhesive microspheres
- Magnetic microspheres
- Diagnostic microspheres
- Therapeutic magnetic microspheres
- Polymeric microspheres.(3)
Materials Used in the Preparation of Microspheres: Polymers are mainly used for the preparation of microspheres. They are classified into two types:
- Natural and
- Synthetic
- Natural polymers are obtained from natural sources like
- a) Carbohydrates: – e.g. Agarose, Chitosan, Carrageenan, and Starch.
- b) Proteins: – e.g. Albumin, Gelatine and collagen
- c) Chemically modified Carbohydrates: -Poly starch, Poly dextran.
- Synthetic polymers are also divided into two types.
- a) Biodegradable polymers: -e.g. Poly anhydrides, glycosides & their copolymers.
- b) Non-biodegradable polymers: – e.g. Glycidyl methacrylate, epoxy polymers. (4, 5)
Various Methods used for Preparation of Microsphere:
- Spray Drying
- Quasi emulsion solvent diffusion
- Double emulsion technique
- Single emulsion technique
- Solvent extraction
- Phase separation coacervation technique
- Spray drying and spray congealing
- Solvent Evaporation (6)
Characterization of Microspheres:
- Particle size and shape(7, 8):
- Determination of Density( 8):
- Dissolution studies( 9):
- Swelling Index( 10):
- Microsphere Morphology:
- Microsphere Size Distribution:
- Yield Values and Loading Efficiency:
- Measurement of Glass Transition Temp (Tg) By Dsc:
- Surface Chemistry by Electron Spectroscopy:
- Release Study:
- Isoelectric Point:
- Degree Of Hydration(11):
Applications of Microspheres:-
- Microcapsules are also extensively used as diagnostics, such as temperature-sensitive microcapsules applicable for thermography detection of tumors.
- In biotechnology, they are used for the production of recombinant proteins and peptides.
- Encapsulation of microbial cells can also increase the cell-loading capacity and the rate of production in bioreactors.
- A feline breast tumor line, which was difficult to grow in conventional culture, has been successfully grown in microcapsules.
- Microencapsulated activated charcoal has been used for hemoperfusion (12).
Materials and Methods:
Extraction of volatile oil:
The cinnamon essential oil was extracted by using hydro distillation with the Clevenger type of apparatus with slight modification. About 30 gm of previously weighed cinnamon bark powder has been put into a 500ml distillation flask with four boiling chips and 300ml of distilled water was poured into the flask they were immersed for 1 Hr followed by heating at 100°C for 6 hr. Then distillate was transformed into a 250 ml conical flask. Then the volatile compounds were extracted from the water phase three times using dichloromethane and dehydrated over anhydrous sodium phosphate for 30 minutes and filtered through a mid-speed filter paper. The cinnamon oil obtained was conc. and stored at 4°C for further analysis. (13, 14)
Preparation of microspheres:
Solvent evaporation method:
- Solvent evaporation is one of the most widely used methods for microsphere preparation.
- For the preparation of the microsphere, Cinnamon oil 1.5ml. (Hydrophobic) was used and further added 1.5gm starch as a polymer to it. (Hydrophilic).
- Then 100ml of cold water was used as a solvent. With continuous stirring further added the 0.5gm Acacia as an emulsifier.
- Using a magnetic stirrer, kept the solution rotating for 15 minutes at 700rpm and then increased the speed up to 1000rpm till 1:30 hour.
- Observed the solution under a microscope. Kept the solution still for 20 minutes until all the particles were settled down.
- Discarded the upper layer of solution and filtered it. Kept the filtrate in the hot air oven for 1 hour at 600Observed the particles under the microscope and evaluated them (6).
Results and Discussion:
Observations and calculations of cinnamon microspheres:
The particle size of the cinnamon microsphere was measured by the micrometric technique in the laboratory.
Observations:
| 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 |
| 2×13=26 | 2×13=26 | 2×13=26 | 1×13=13 | 2×13=26 |
| 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 2×13=26 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 |
| 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 |
| 1×13=13 | 2×13=26 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 | 1×13=13 |
Calculation :( 14)
1 division on eye piece = 0.01nm division on stage micrometre = 10 µm
⁖10 divisions on eye piece =13 divisions on stage micrometre
⁖ 10 divisions =13 × 10=130µm
⁖ 1 division = x
| ⁖ | x = 130÷10 | |
| ⁖ | x = 13 µm |
Mean=403÷25
=16.12µm
Therefore, one microsphere’s diameter is 16.12 µm.
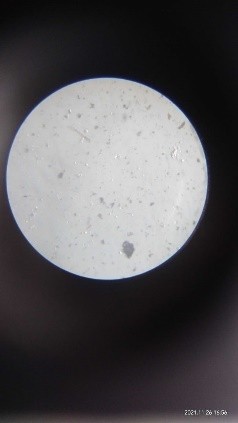

Cinnamon oil under microspheres Cinnamon oil microspheres
Conclusion:
The Literature review shows that microspheres are the prominent choice of the delivery system because it decreases the dose frequency and also shows enhanced dissolution rate, bioavailability, and stability. Additionally helps to deliver the Pharmaceutical ingredient to the desired sites in the body. In succeeding years the herbal microsphere novel drug delivery system which is efficacious in cancer therapy or in any other disease related to the cardiac system, nervous system, and pulmonary system. The herbal microsphere formulation shows more effectual results in the in-vivo delivery system. Microspheres were evaluated for particle size and shape. The particle size was found to be 16.12 µm and the shape was spherical. On the basis of our research, we concluded that the herbal microspheres of Cinnamon were prepared by the Solvent Evaporation Method could help to researchers for further study.
References:
- Tariq Jamshaid, 5th International Conference and Exhibition on Pharmaceutical Regulatory Affairs, August 03-05, 2015.
- Mahale Manisha M, Saudagar R B, Microsphere: A Review, Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics. 2019; 9(3-s):854-856
- Ritu Verma, Shubham Verma, Sokindra Kumar, Microsphere–A Novel Drug Delivery System, Research Chronicle in Health Sciences 2019;5(1):5-14 ISSN 2395-552X.
- Kumar A, Mahajan S, Bhandari N. Microspheres: a review. World J Pharm Pharm Sci.,14;6:724-40(2017)
- Rajput S, Agrawal P, Pathak A, Shrivasatava N, Baghel SS, Baghel RS. A review on microspheres: methods of preparations and evaluation. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1:422-38 (2012)
- Ananta Choudhury, Debasish Deka, Kashmiri Sonowal, Rahela Eyachmin Laska, Microsphere: a promising approach for drug delivery, Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Research Volume 7, Issue 2, Year of Publication 2019, ISSN: 2348 – 0335.
- Ramteke K.H, Jadhav V.B, Dhole S.N. Microspheres: as carriers used for novel drug delivery system. Iosrphr, 2 (4): 44-8 (2012)
- Nagoba Shivappa N., Chandrawanshi Mayuri J., Bhalekar Rohini V, Viayjendra Swamy S. M.A Review on Microspheres as a Novel Drug Delivery. System. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Research, (2018)
- Prasad BS, Gupta VR, Devanna N, Jayasurya K. Microspheres as drug delivery system-a review. J Glob Trends Pharm Sci., 5:1961-72 (2014)
- Sharma N, Purwar N, Gupta PC. Microspheres as drug carriers for controlled drug delivery: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research; 6(11): 4579(2015).
- https://www.slideshare.net/shikha Swetha/microspheres
- https://www.slideshare. net/thilak051/microspheres-13875950
- Practical Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry by Dr. Tulsidas Nimbalkar Pee Vee publication Page No.13
- Practical Pharmacognosy by K . R . Khandelwal, Nirali Prakashan, 17th edition. Page No.- 103
