1 Anshul Srivastava , 2Abhishek Srivastava,3Sohit Agarwal, 4Gajanand Sharma
1.Undergraduate Scholar (ECE) Bhagwant University, Ajmer
2.Undergraduate Scholar (CSE)Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur
3,4(Assistant Professor)
(Department of Computer Science and Engineering)
Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur
Abstract:-Cloud computing provides the facility to access shared resources and common infrastructure, offering services on demand over the network to perform operations that meet changing business needs. The location of physical resources and devices being accessed are typically not known to the end user. It also provides facilities for users to develop, deploy and manage their applications „on the cloud‟, which entails virtualization of resources that maintains and manages itself. Cloud computing, a computing platform for the next generation of the Internet. It also defines clouds, explains the business benefits of cloud computing, and Outlines cloud architecture and its major components. “Cloud Computing” also known as grid, large-scale distributed, or Internet-scale computing
Keywords:-IaaS,PaaS,SaaS,Grid computing and utility computing
I .INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is a term used to describe both a platform and type of application. A cloud computing platform dynamically provisions, configures, reconfigures, and deprovisions servers as needed. Servers in the cloud can be physical machines or virtual machines. Advanced clouds typically include other computing resources such as storage area networks (SANs), network equipment, firewall and other security devices. Cloud computing also describes applications that are extended to be accessible through the Internet. These cloud applications use large data centers and powerful servers that host Web applications and Web services. Anyone with a suitable Internet connection and a standard browser can access a cloud application.
various restrictions or trade-offs that may be a non-starter for war project.
II.COMPUTING ARCHITECTURE
Cloud computing system is divided into two sections: the front end and the back end. They connect to each other through a network, usually the The front end is the side the computer user, or client, sees.The back end is the “cloud” section of the system.The front end includes the client’s computer (or computer network) and the application required to access the cloud computing system. Not all cloud computing systems have the same user interface. On the back end of the system are the various computers, servers and data storage systems that create the “cloud” of computing services. Cloud computing system could include practically any computer program we can imagine, from data processing to video games. Usually, each application will have its own dedicated server.
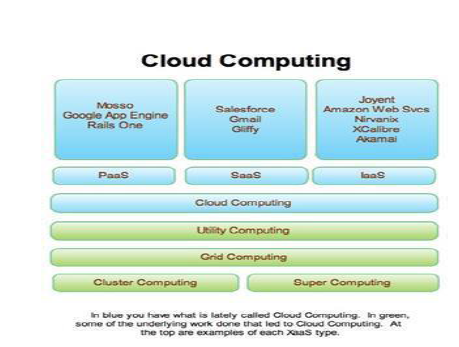
III. CLOUD COMPUTING SERVICES
IaaS: IaaS clouds make it very easy and affordable to provision resources such as servers, connections, storage, and related tools necessary to build an application environment from scratch on-demand. IaaS clouds are the underlying infrastructure of PaaS and SaaS clouds. IaaS clouds are more complex to work but with that complexity comes a high degree of flexibility. The number one benefit of such services is rapid provisioning. Billing for these services is usually incremental by use and can get complex with tiered on-demand pricing that can be difficult to track in real time. Pricing is usually well defined but can be rather difficult to forecast in some cases.
PaaS: PaaS clouds are designed, often within IaaS Clouds by experts to make the deployment and scalability of war application trivial and war costs incremental and reasonably predictable. Some of the few choice Application Stack Cloud Providers (ASCP) are Google App Engine, Python SalesForce– Proprietary ,Morph – Ruby on Rails,Heroku – Ruby on Rails. There are more and more PaaS clouds sprouting up constantly and rapidly.
SaaS: Software as a Service has been around for a while now and actually precedes the newer term Cloud Computing. Cloud Computing is breathing ever more life into the SaaS model by reducing the costs associated with producing a SaaS application. A couple of well known examples of SaaS are Gmail or SalesForce. The number one down side of choosing an PaaS Cloud provider is that all such services come with
IVRELATED TECHNOLOGIES
Cloud computing’ is relatively new, but the technologies that make it possible have been used for some time. For example, cloud computing is enabled by grid computing, virtualization, utility computing, hosting and software as a service (SaaS). Yet these technologies differ from cloud computing in the some ways given below:
Grid Computing: Originally designed for computationally intensive batch applications, grid computing was developed as a way to share computers and data. From these beginnings, modern grid computing technologies have evolved as a way to harness inexpensive servers in a data center to solve a variety of business problems. Traditionally, grids have lacked the automation, agility and simplicity characterized by cloud computing.
Utility computing: In the utility computing model, computing resources like applications, infrastructure and storage are packaged and sold as a service, with users paying only for what they consume, like electricity. In many respects, cloud computing is closely related to the utility computing model, with cloud computing being a broader concept that relates to the underlying architecture in which the services are designed.
Virtualization: Virtualized infrastructures are available on-demand and capable of supporting multiple users, but lack the automation required for the self-managing, self-healing property of the cloud. Hosting: Hosting services provide space on servers for use by clients as well as providing IP-based connectivity, typically in a data center. Because hosting does not enable on-demand, elastic scalability, it cannot be considered cloud computing.
SaaS: Although Software-as-a-Service offerings are often hosted on true clouds, SaaS is an application as a service and cloud computing is IT infrastructure as a service
V.TYPES OF CLOUDS
Public clouds: This environment can be used by the general public. This includes individuals, corporations and other types of organizations. Typically, public clouds are administrated by third parties or vendors over the Internet, and services are offered on pay-per-use basis. These are also called provider clouds. Business models like SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) and public clouds complement each other and enable companies to leverage shared IT resources and services. The main benefits of public clouds is that they are widely used in the development, deployment and management of enterprise applications, at affordable costs and allows organizations to deliver highly scalable and reliable applications rapidly and at more affordable costs. But Security is a significant concern in public clouds Private clouds: This cloud computing environment resides within the boundaries of an organization and is used exclusively for the organization’s benefits. These are also called internal clouds. They are built primarily by IT departments within enterprises who seek to optimize utilization of infrastructure resources within the enterprise by provisioning the infrastructure with applications using the concepts of grid and virtualization. The main benefits of private clouds is that they improve average server utilization; allow usage of low-cost servers and hardware while providing higher efficiencies; thus reducing the costs that a greater number of servers would otherwise entail and they hava high levels of automation, reducing operations costs and administrative overheads.But IT teams in the organization may have to invest in buying, building and managing the clouds independently
External clouds: This cloud computing environment is outside of the boundaries of the organization, though it is not necessarily a public cloud. Some external clouds make their cloud infrastructure available to specific other organizations, but not to the general public.
Hybrid clouds: This is a combination of both private (internal) and public (external) cloud computing environments.
VI.CONCLUSION
In today’s global competitive market, companies must innovate and get the most from its resources to succeed. This requires enabling its employees, business partners, and users with the platforms and collaboration tools that promote innovation. Cloud computing infrastructures are next generation platforms that can provide tremendous value to companies of any size. They can help companies achieve more efficient use of their IT hardware and software investments and provide a means to accelerate the adoption of innovations. Cloud computing increases profitability by improving resource utilization. Costs are driven down by delivering appropriate resources only for the time those resources are needed. Cloud computing has enabled teams and organizations to streamline lengthy procurement processes. Cloud computing enables innovation by alleviating the need of innovators to find resources to develop, test, and make their nnovations available to the user community. Innovators are free to focus on the innovation rather than the logistics of finding and managing resources that enable the innovation. Combining cloud computing with IBM Innovation Factory provides an end-to-end collaboration environment that could transform organizations into innovation power houses. IBM is a leader in cloud computing and innovation technologies.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Authors are thankful to Mr. Ankur Goyal HOD, CSE Deptt, yagvalakya Institute of Engineering & Technology, Jaipur for granting permission to publish this paper.

