pp 29-31
Pramod Singh1, Anish Mohammad2
1Chief Librarian, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur (Raj)
2Dy. Librarian, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur (Raj)
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to examine the present status of digitization of Indian regional libraries, conditions, challenges they faced to pose effective information delivery as well as technologies aspect. The Indian regional libraries have digitized and working as information hubs also with the help of technology based resources and services. The digital library stores digital objects and representing different types of information. Older collections are now digitized through a conversion process whereas documents in paper format are converted into electronic format. Converting texts in different languages requires careful consideration of character sets. Unicode provides process a standard scheme for universally acceptable format. This paper presents a critical analysis of the recent status of digitization of Indian Libraries.
Keywords – ICT, Information Seeking Behaviour, Information Retrieval System, UNICODE, World Wide Web, RFID, etc.
- Introduction
A Library is a collection of information, sources, resources, books, and services, and the structure in which they resides. The information is an important part of the knowledge, without libraries, we cannot imagine technology oriented knowledge based society. In the library, we can preserve our Past, Present and Future also because all types of libraries are played important role in the society from the Academic, Public, and Research also.
2. Evolution of Regional Libraries: An Indian Perspective
Libraries have played important role in the field of knowledge as well as information seeking behaviour and user satisfaction of the national and international level. The Information literacy is grounded in a belief that there are compressive and universally applicable standards both for information behaviour and information literacy. Libraries have developed in concert with their local and national history. There are Political, economic and social circumstances to develop libraries. One can easily find diversity and difference among libraries. The most modern and well-equipped library is not necessarily the most developed in the art of stimulating popular participation as examples can be found all over the world.
In India, the regional library concept came from the public library mission since pre- independence, because the libraries had classified and divided in zone-wise manner. All over India, libraries were classified in the five Zones/Regions i.e Eastern, North – Central, Northern, Western and Southern. But the regional libraries had called of divisional libraries, but both are same. The trend to procure and maintain E-resources had grown exponentially among the libraries. This is due to change in the information seeking behaviour of the libraries members. They are showing greater interest on E–resources, and, libraries and publishers cater to their requirements by providing same. This has been revealed by many survey findings. In the print environment the methods of appraisal, accessioning, organising, describing, preserving are clearly defined for archiving and preserving.
3. Digitization of libraries in India: An analysis
The Digitization is required for improving the efficiency of services to deliver at all levels as well as regional libraries also. The direct access to this huge source of information can be making available all over the world by digitization of regional libraries in India. Digital library is a way of making information retrieval system as well as information seeking behaviour and user friendly also. The digitization presentation poses lots of problems due to fast pace of technology development, fragility of digital information and computing infrastructure also. Time seems right for Indian libraries to explore various options to create models for digital preservation of E-resources subscribed by them. The various consortia of the country – INDEST, INFLIBNET initiated digital preservation projects which may be modelled on LOCKSS and CLOCKSS.
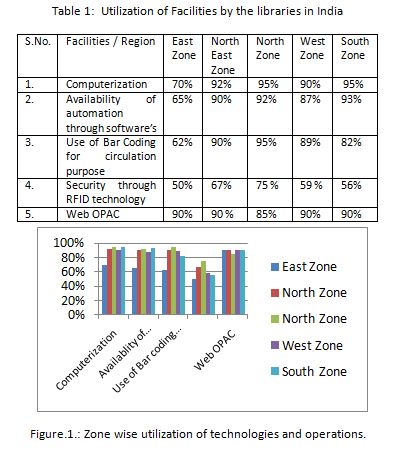
Figure 1 presented the utilization of technologies and other operations. Regional libraries having GIAN (Global Initiative of Academic Network) steps for the development of information systems and utilization of information resources and also for introducing computer based decision support system.
4. Conclusion
Digitization is being carried on long scale, world-wide to facilities and ensures wider dissemination and access of Information. The increasing use of the internet and World Wide Web (web) has developed awareness and concerns about access and retrieval of information across networks. Libraries are in midpoint how to satisfy the hunger of the new generation to get Information. Digitization is crucial for preserving and disseminating information and knowledge effectively and efficiently. ICT has touched all the fields directly or indirectly in today’s world. Innovations in Information Technology have brought radical changes in every possible field of life including Libraries. The library is, and always has been, the heart of an academic society. This area is also of paramount importance for assessing the existing Indian regional Libraries and creating highly user – Centric Regional Libraries in India.
References
- Sharma, Neelam (2012), “Automation and Digitization in University Libraries: A Comparative Study of Seven North Indian University Libraries”, International Journal of Information Dissemination and Technology, Vol.2 (2), pp.135-141.
- Patil, Varsha (2013),”Library Automation and Networking: Need and Importance of Maharashtra Public Libraries”, Journal of Advances in Library and Information Science, Vol.2 (3), pp.152 – 156.
- Janakiraman, C (2011),”Modern Library System”, Delhi, Pacific Books International, ISBN 9789380472256, pp. 1- 15.
- Mahesh, G & Rekha Mittal, (2008), “Digital Libraries in India: A Review”, Libri, Vol. 58.pp. 15 – 24.
- Hulser, Richard P. (1997),”Digital Library: Content Preservation in a Digital World”, DESIDOC Bulletin of Information Technology, Vol. 17 (6), pp.7-14.
- Gaur, R. C. & Manorama Tripathi (2012),”Digital Preservation of Electronic Resources”, DESIDOC Journal of Library & information Technology, Vol. 32 (4), pp. 293 – 301.
