DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT FOR CO2 LASER MACHINING OF CFRP BY USING RESPONSE SURFACE METHODOLOGY (RSM)
¹Alok Sharma, ²Amit Tiwari, ³HimanshuVasnani
¹M.Tech Scholar, ² ³Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur, India
ABSTRACT
This paper discusses about design of experiments for CO2 laser machining by RSM technique. Design of experiment (DOE) is an efficient method to plan experiments so that the output data can be analyzed. Response surface methodology is a technique to determine the relationship between various process parameters with various machining parameters and predicts the effects of these process parameters on the response of the process. Carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) is a composite material which is made by adding carbon fibre and epoxy resin together. In this paper, design of experiments for CO2 laser machining of 1mm CFRP sheet by using a low power CO2 laser (150w) and low cutting speed (1mm/sec) by response surface methodology was investigated.
Keywords: DOE, Response Surface Methodology, CFRP etc.
- INTRODUCTION
1.1 Design of Experiment
Design of experiments (DOE) is an approach to find out most affecting factor in a process. In other words, it is a basis for any optimization technique. Design of experiments (DOE) is a systematic, accurate approach to solve the engineering problem that applies principles and techniques at the data collection stage so as to obtain valid, feasible output. By this design of experiment, optimization is carried out to analyze the whole process effectively.
Figure 1: Design of Experiment Chart
Design of experiments can be predicted by many techniques like Taguchi method, Response Surface Methodology and ANOVAs method. In this research, Response Surface Methodology was used to analyze output parameters.
1.2 CO2 Laser Machining
The laser beam is very narrow and different from the normal luminous beam due to its narrow spectral band. Here the light amplification is achieved by a pumping system which consists of two mirrors. In laser machining, the laser beam energy is absorbed by the material surface when interaction occurs between laser beam and material surface. This laser machining consists of CO2, Nitrogen and Helium gas as a assist gas.
1.3 Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
Response Surface Methodology (RSM) is an optimization tool for analysis of data and prediction of optimal results, which are directly related to desired output.
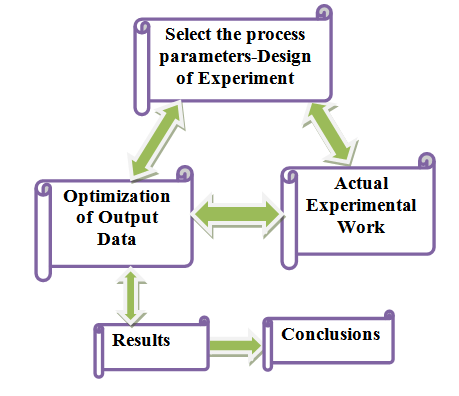
Figure 2: Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Chart
The basic steps of the Response surface methodology are:
- Select the process parameters and design of experiment according efficient runs.
- Perform actual experimental work according to design of experiment.
- Validate the output data.
- Optimize the output data with optimization software like MINITAB.
- Find the optimum level of process and generate results and conclusions.
1.4 Selecting the Level [2]
(i)Two level (2k)-(-1, +1)2k) – (-1)-first
Two-level factorial design is evaluated at a “lower” and “higher” level.
(ii)Three level (3k)-(-1, 0, +1) (3k) – (-11) second or higher order
Three-level factorial design is evaluated at a “lower”, “center” and at “higher” level.
(iii)Five level (5k)-(-a,-1, 0, +1, +a) (5k)-(-α, -1,0,+1, -α) second or higher or
Five-level factorial design is evaluated at a “alpha lower”, “lower”, “center” , “higher” and “alpha higher” level.
1.5 Selecting the Type of DOE
- Full factorial design
- Fractional factorial design
- Central composite design
- Box-behnken design
These are the DOE based on response surface methodology but fractional factorial design was used because:
- It has very simple design
- Less experimental work is needed because of less runs performed.
- This design can show the effective results by graphs.
- Results can be drawn by less runs and experimental work.
- LITERATURE REVIEW
[1] A. Salama1• L. Li1• P. Mativenga1• D. Whitehead1-(2016)-Springer: Response Surface Methodology was used to analyze the process parameters to determine HAZ, machining depth and material removal rate (MRR).
[2] Wan Nor Nadyaini Wan Omar-(2015)– this paper describes the various response surface methodology like full factorial design, box-behnken design etc.
[3] A. Riveiro, F. Quintero, F. Lusquinos, J. Del Val, R. Comesana, M. Boutinguiza, J. Pou-(2012)- Elsevier: This paper shows that laser power is the most affecting factor for generation of Kerf width and erosion in entry side.
[4] Johannes Stock, Michael F. Zaeh, Markus Conrad -(2012)- Elsevier– Remote laser cutting of CFRP was studied in this paper. This paper deals with effect of material properties on cutting process. It can be beneficial to fuse light absorbing particles to composite matrix so that cutting process can be improved with less surface defects.
[5]K. Palani kumar-(2008)– This paper describes Application of response surface methodologies and Taguchi method to determine surface roughness in machining glass fiber reinforced plastics by PCD tooling.
- METHODOLOGY
3.1 Fractional Factorial Design
| A | B | C | |
| 1 | -1 | -1 | -1 |
| 2 | +1 | -1 | -1 |
| 3 | -1 | +1 | -1 |
| 4 | +1 | +1 | -1 |
| 5 | -1 | -1 | +1 |
| 6 | +1 | -1 | +1 |
| 7 | -1 | +1 | +1 |
| 8 | +1 | +1 | +1 |
Table 1:2-level fractional design
Where
-1= lower level
+1= higher level
I have used 2-level and 3 parameters-
Process Parameters
- Laser power( Watt)
- Cutting speed (mm/sec.)
- Gas pressure ( bar)
- Final Design of Experiment
| No. of experiments | Laser power(W) | Cutting speed (mm/sec.) | Gas pressure(bar) |
| 1. | 120 | 1 | 1 |
| 2. | 150 | 1 | 1 |
| 3. | 120 | 2 | 1 |
| 4. | 150 | 2 | 1 |
| 5. | 120 | 1 | 2 |
| 6. | 150 | 1 | 2 |
| 7. | 120 | 2 | 2 |
| 8. | 150 | 2 | 2 |
Table 2: Design of Experiment for Experimental Work
- Optimization of the Process
Minitab Software-
It is software to design and analyze data. RSM optimization can be done by this software so I have used this software for optimization.
- CONCLUSIONS
In this research, response surface methodology was used effectively to analyze and optimize output data. RSM helps to obtain maximum affecting factor for output of machining process. This technique helps in reduction of experimental runs. MINITAB software is simple software for optimization purpose. The full factorial design is an economical design to reduce overall experimental work. It was found that laser power is most affecting factor for output of machining process and 150w CO2 laser can cut 1mm CFRP sheet.
REFERENCES
[1]. Salama1 L. Li1,P. Mativenga1,D. Whitehead1- TEA CO2 laser machining of CFRP composite -Appl. Phys. A (2016) 122:497
[2]Design Of Experiment (DOE) & Response Surface Methodology (RSM): Wan Nor Nadyaini Wan Omar-2015
[3]Overview on the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in Extraction Processes-2015
[4]Parametric optimization during wire electrical discharge machining using response surface methodology Pragya Shandilya, P.K. Jain, N.K. Jain-2012
[5]Riveiro, F. Quintero , F. Lusquinos, J. Del Val , R. Comesana, M. Boutinguiza, J. Pou, “Experimental Study On The CO2Laser Cutting Of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastic Composite”, Composites: Part A ,Vol-43, Pp:1400–1409, 2012
[6] Johannes Stock,Michael F. Zaeh, Markus Conrad, “Remote Laser Cutting Of CFRP: Improvements in the cut surface-2012
[7] Response Surface Methodology: An Overview-Ashwin Pathak , Dr. Vijaya Kumar K.N
[8]Satpal Sharma; Flank Wear Prediction Model Development by Response Surface Methodology; Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol. 3, Issue 1, Jan-Jun 2013.
[9]H. Yanda, J.A. Ghani, M.N.A.M. Rodzi, K. Othman And C.H.C. Haron, Optimization Of Material Removal Rate, Surface Roughness And Tool Life On Conventional Dry Turning Of Fcd700, International Journal Of Mechanical And Materials Engineering (Ijmme), Vol.5 (2010), No.2, 182-190
[10]K. Palani kumar, Application of Taguchi and response surface methodologies for surface roughness in machining glass fiber reinforced plastics by PCD tooling, The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, February 2008, Volume 36, Issue 1-2, pp 19-27.
